What You Will Learn:
Structures
Arrays help us to store similar type of values in contiguous locations in the memory. Using arrays we cannot store different type of values in a single array.
Def: Structure is a special derived data type which helps us to combine data items belonging to different data types and represent them as a single logical unit.
Keyword “struct” is used to declare a structure
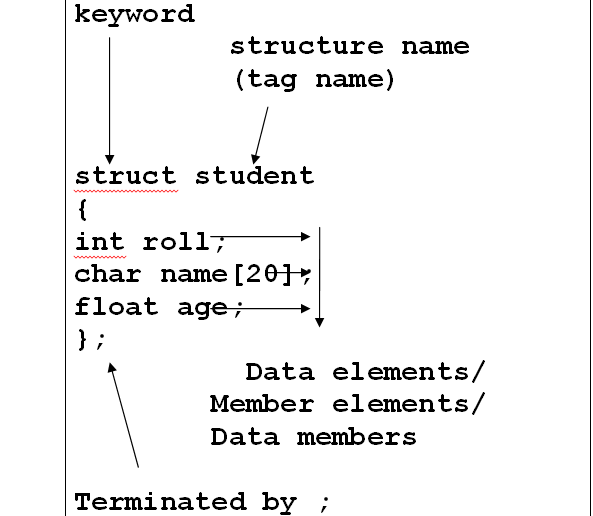
In the above example, “student” is the name of the structure, it is also known as the tag name.
This tag name is used to declare the structure variables in the program, which are used in the programming.
The (roll,name and age) are called as the data elements /member elements/data members/attributes /properties of the structure.
The data elements are declared independently within the definition of the structure.
The definition of the structure is terminated by a semicolon.
The above structure definition is just a template. It cannot be used independently in the program. We have to declare structure variables of type defined structure and then use them while programming.(As the structure does not occupy any memory by itself, whereas the structure variable does.)
Declaration of structure variable
(a)
Single structure variable declaration
struct student s;
| s |
| Roll Name Age |
(b)
Multiple structure variable declaration
struct student s1,s2,s3;
| s1 | s2 | s3 |
| Roll Name Age |
Roll Name Age |
Roll Name Age |
(c)
Array type structure variable declaration
struct student s[10];
|
S[0] |
S[1] |
S[2] |
S[3] |
S[4] |
S[5] |
|
|
|
S[9] |
|
Roll Name Age |
Roll Name age |
Roll Name age |
Roll Name Age |
Roll Name age |
|
|
|
|
Roll Name age |
The data elements of the structure / structure variable are accessed using . (dot operator)
Example:
struct student s;
scanf(“%d”,&s.roll);
scanf(“%s”,s.name);//gets(s.name);
scanf(“%f”,&s.age);
The size of a structure/structure variable is equal to the sum of the sizes of all data elements.
sizeof(): this function helps us to find the size of a data type or a variable.
int a;
printf(“%d”,sizeof(int)); // 2
printf(“%d”,sizeof(a)); // 2
struct student s;
printf(“%d”,sizeof(struct student)); // 26 (2+20+4)
printf(“%d”,sizeof(s)); // 26 (2+20+4)
Note: Size of a structure with no data element is always one byte.
struct student
{
};
struct student s;
printf(“%d”,sizeof(struct student)); // 1
printf(“%d”,sizeof(s)); // 1




