Network topologies
Network topologies and types
Network topology
- Computer networks may be classified according to the network topology upon which the network is based, such as Bus network, Star network, Ring network, Mesh network, Star-bus network, Tree or Hierarchical topology network, etc.
- Network Topology signifies the way in which intelligent devices in the network see their logical relations to one another.
Star Topology
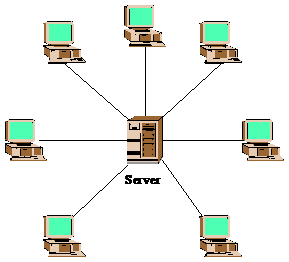
The type of network topology in which each of the nodes of the network is connected to a central node with a point-to-point link in a ‘hub’ and ‘spoke’ fashion, the central node being the ‘hub’ and the nodes that are attached to the central node being the ‘spokes’ (e.g., a collection of point-to-point links from the peripheral nodes that converge at a central node) – all data that is transmitted between nodes in the network is transmitted to this central node, which is usually some type of device that then retransmits the data to some or all of the other nodes in the network, although the central node may also be a simple common connection point (such as a ‘punch-down’ block) without any active device to repeat the signals.
Bus Topology
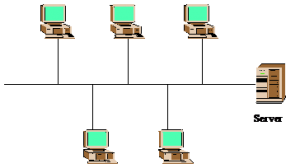
The type of network topology in which all of the nodes of the network are connected to a common transmission medium which has exactly two endpoints (this is the ‘bus’, which is also commonly referred to as the backbone, or trunk) – all data that is transmitted between nodes in the network is transmitted over this common transmission medium and is able to be received by all nodes in the network virtually simultaneously (disregarding propagation delays).
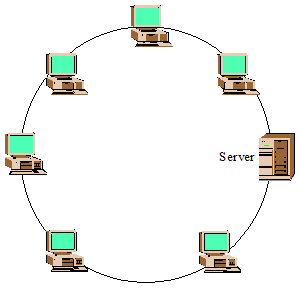
Ring Topology
The type of network topology in which each of the nodes of the network is connected to two other nodes in the network and with the first and last nodes being connected to each other, forming a ring – all data that is transmitted between nodes in the network travels from one node to the next node in a circular manner and the data generally flows in a single direction only.
Mesh Topology
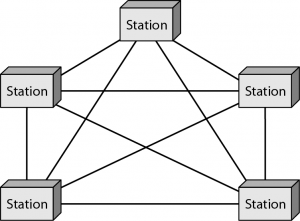
The value of fully meshed networks is proportional to the exponent of the number of subscribers, assuming that communicating groups of any two endpoints, up to and including all the end points.